Can Young Athletes Take Creatine?

Let’s break down what creatine is, how it’s used, and if it’s safe for your teen athlete to use.
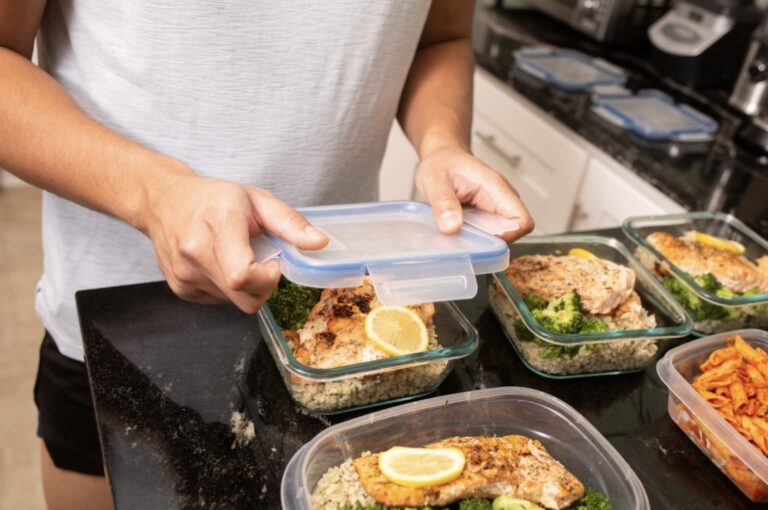





For athletes, proper nutrition is the cornerstone of peak performance. Whether you’re a student athlete, seasoned competitor, or a weekend warrior, meal prepping can be a game-changer when it comes to meeting your nutritional needs. Here are five key tips…

Amenorrhea & Athletes: 3 Tips For Females to Get Their Period Back Relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S) is the consequence of low-energy availability (LEA) in athletes, adversely affecting an athletes’ performance and health. RED-S can occur in both…